BeanFactoryPostProcessor工作在Bean实例化之前,BeanPostProcessor工作在Bean初始化方法前后。
BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanPostProcessor,这两个接口,都是Spring初始化bean时对外暴露的扩展点。两个接口名称看起来很相似,但作用及使用场景却不同,分析如下:
1. BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口
该接口的定义如下:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
/**
* Modify the application context's internal bean factory after its standard
* initialization. All bean definitions will have been loaded, but no beans
* will have been instantiated yet. This allows for overriding or adding
* properties even to eager-initializing beans.
* @param beanFactory the bean factory used by the application context
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
*/
void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException;
}
实现该接口,可以在spring的bean创建之前,修改bean的定义属性。也就是说,Spring允许BeanFactoryPostProcessor在容器实例化任何其它bean之前读取配置元数据,并可以根据需要进行修改,例如可以把bean的scope从singleton改为prototype,也可以把property的值给修改掉。可以同时配置多个BeanFactoryPostProcessor,并通过设置’order’属性来控制各个BeanFactoryPostProcessor的执行次序。
注意:BeanFactoryPostProcessor是在spring容器加载了bean的定义文件之后,在bean实例化之前执行的。接口方法的入参是ConfigurrableListableBeanFactory,使用该参数,可以获取到相关bean的定义信息。
2. BeanPostProcessor接口
该接口的定义如下:
public interface BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* Apply this {@code BeanPostProcessor} to the given new bean instance <i>before</i> any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.
* <p>The default implementation returns the given {@code bean} as-is.
* @param bean the new bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one;
* if {@code null}, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
*/
@Nullable
default Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
/**
* Apply this {@code BeanPostProcessor} to the given new bean instance <i>after</i> any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.
* <p>In case of a FactoryBean, this callback will be invoked for both the FactoryBean
* instance and the objects created by the FactoryBean (as of Spring 2.0). The
* post-processor can decide whether to apply to either the FactoryBean or created
* objects or both through corresponding {@code bean instanceof FactoryBean} checks.
* <p>This callback will also be invoked after a short-circuiting triggered by a
* {@link InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation} method,
* in contrast to all other {@code BeanPostProcessor} callbacks.
* <p>The default implementation returns the given {@code bean} as-is.
* @param bean the new bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one;
* if {@code null}, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean
*/
@Nullable
default Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
}
BeanPostProcessor,可以在spring容器实例化bean之后,在执行bean的初始化方法前后,添加一些自己的处理逻辑。这里说的初始化方法,指的是下面两种:
1)bean实现了InitializingBean接口,对应的方法为afterPropertiesSet
2)在bean定义的时候,通过init-method设置的方法
注意:BeanPostProcessor是在spring容器加载了bean的定义文件并且实例化bean之后执行的。BeanPostProcessor的执行顺序是在BeanFactoryPostProcessor之后。
3. 实战
BeanFactoryPostProcessor
public class MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("1. 调用BeanFactoryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanFactory");
BeanDefinition bd = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition("myJavaBean");
MutablePropertyValues pv = bd.getPropertyValues();
pv.addPropertyValue("remark", "BeanFactoryPostProcessor中修改之后的remark");
}
}
BeanPostProcessor
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if ("myJavaBean".equals(beanName)){
System.out.println("3. 调用BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization");
}
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if ("myJavaBean".equals(beanName)){
System.out.println("7. 调用BeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization");
}
return bean;
}
}
配置类
@Configuration
public class MyConfig {
@Bean(initMethod = "initMethod", destroyMethod = "destroyMethod")
public MyJavaBean myJavaBean() {
MyJavaBean bean = new MyJavaBean();
bean.setRemark("原始remark");
return bean;
}
@Bean
public MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor myBeanFactoryPostProcessor(){
return new MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor();
}
@Bean
public MyBeanPostProcessor myBeanPostProcessor(){
return new MyBeanPostProcessor();
}
}
Bean
public class MyJavaBean implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
private String desc;
private String remark;
public MyJavaBean() {
System.out.println("2 Bean的无参构造函数");
}
public MyJavaBean(String desc, String remark) {
this.desc = desc;
this.remark = remark;
System.out.println("2 Bean的全参构造函数");
}
@PostConstruct
public void postConstruct() {
System.out.println("4. 调用PostConstruct方法");
}
public String getDesc() {
return desc;
}
public void setDesc(String desc) {
System.out.println("调用setDesc方法");
this.desc = desc;
}
public String getRemark() {
return remark;
}
public void setRemark(String remark) {
System.out.println("调用setRemark方法");
this.remark = remark;
System.out.println("remark = " + this.remark);
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("5. 调用InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet方法");
this.desc = "afterPropertiesSet中修改之后的desc";
}
public void initMethod() {
System.out.println("6. 调用Bean的init方法");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("8. 调用DisposableBean.destroy");
}
public void destroyMethod() {
System.out.println("9. 调用Bean的destroy方法");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
builder.append("[desc:").append(desc);
builder.append(", remark:").append(remark).append("]");
return builder.toString();
}
}
启动类
@SpringBootApplication
public class PostProcessorApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = SpringApplication.run(PostProcessorApplication.class, args);
MyJavaBean bean = (MyJavaBean) applicationContext.getBean("myJavaBean");
System.out.println("=======================结果====================");
System.out.println("desc:" + bean.getDesc());
System.out.println("remark:" + bean.getRemark());
System.out.println("======================结果====================");
}
}
执行顺序:
1. 调用BeanFactoryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanFactory
2 Bean的无参构造函数
调用setRemark方法
remark = 原始remark
调用setRemark方法
remark = BeanFactoryPostProcessor中修改之后的remark
******beanName = myJavaBean
******beanFactory = org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory
******applicationContext = org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
3. 调用BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization
4. 调用PostConstruct方法
5. 调用InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet方法
6. 调用Bean的init方法
7. 调用BeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization
=======================结果====================
desc:afterPropertiesSet中修改之后的desc
remark:BeanFactoryPostProcessor中修改之后的remark
======================结果====================
8. 调用DisposableBean.destroy
9. 调用Bean的destroy方法
BeanFactoryPostProcessor对Bean属性的修改延迟到了Bean初始化完成之后才执行
4. 进一步深入分析
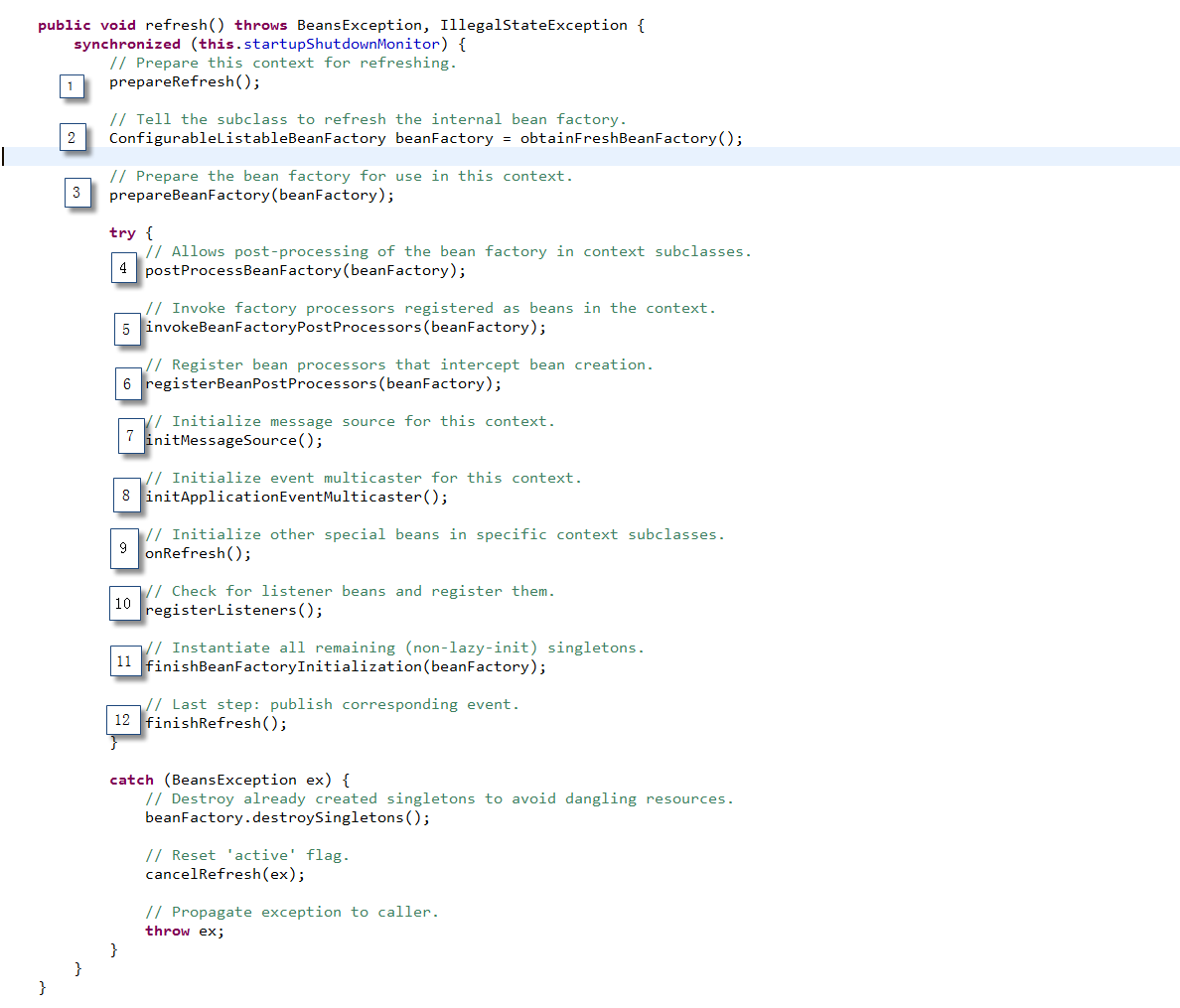
在使用ApplicationContext启动spring容器的时候,在AbstractApplicationContext.refresh()方法中,完成相关初始化工作:
1)BeanFactoryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory,是在第5步执行的
2)而BeanPostProcessor的执行,取决于配置文件中bean的定义,如果定义的bean是singleton并且不是抽象类,也不延迟初始化,则BeanPostProcessor是在第11步中执行;而对于prototype的bean,BeanPostProcessor是在程序getBean的时候执行的。在第6步中,调用registerBeanPostProcessors方法,注册所有实现BeanPostProcessor接口的bean
5. 总结
- 创建(调用构造函数)
- set属性(set方法注入属性)
- 判断是否实现BeanNameAware接口,并调用接口的setBeanName方法
- 判断是否实现BeanFactoryAware接口,并调用接口的setBeanFactory方法
- 判断是否实现ApplicationContextAware接口,并调用接口的setApplicationContext方法
- 判断是否实现BeanPostProcessor接口,并调用接口的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法
- 判断是否实现InitializingBean接口,并调用接口的afterPropertiesSet方法
- 判断是否自定义init方法,并调用
- 判断是否实现BeanPostProcessor接口(同6),并调用接口的postProcessAfterInitialization方法
- 业务代码中Bean对象的使用
- 当容器销毁时,判断是否实现DisposableBean接口,并调用接口的destroy方法
- 判断是否自定义销毁方法,并调用
对于 BeanNameAware BeanFactoryAware ApplicationContextAware 这3个接口我们平时很少实现它,一般用于让Bean能够感知到BeanName BeanFactory ApplicationContext
public class MyJavaBean implements BeanNameAware, BeanFactoryAware, ApplicationContextAware {
private String beanName;
private BeanFactory beanFactory;
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Override
public void setBeanName(String s) {
this.beanName = s;
System.out.println("******beanName = " + this.beanName);
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
System.out.println("******beanFactory = " + this.beanFactory);
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
System.out.println("******applicationContext = " + this.applicationContext);
}
}


评论